Romanticism in art was a transformative and influential movement that emerged in late 18th-century Europe. It marked a departure from the rationalism of the Enlightenment era and celebrated emotions, individualism, and the profound power of nature.
Romantic artists sought to evoke intense feelings, often depicting awe-inspiring natural landscapes and exploring the sublime.
The movement embraced a wide range of themes, including national identity, heroism, exoticism, and a revival of medieval aesthetics.
Romanticism left a lasting impact on art, literature, and culture, emphasizing the importance of imagination and the unique human spirit.
Romanticism Facts
1. Emerged in late 18th century Europe
Romanticism as an artistic and intellectual movement emerged in the late 18th century in Europe. It was a response to the Enlightenment, which emphasized reason, logic, and rationality.
Romantics, on the other hand, sought to emphasize the emotional, imaginative, and subjective aspects of human experience.
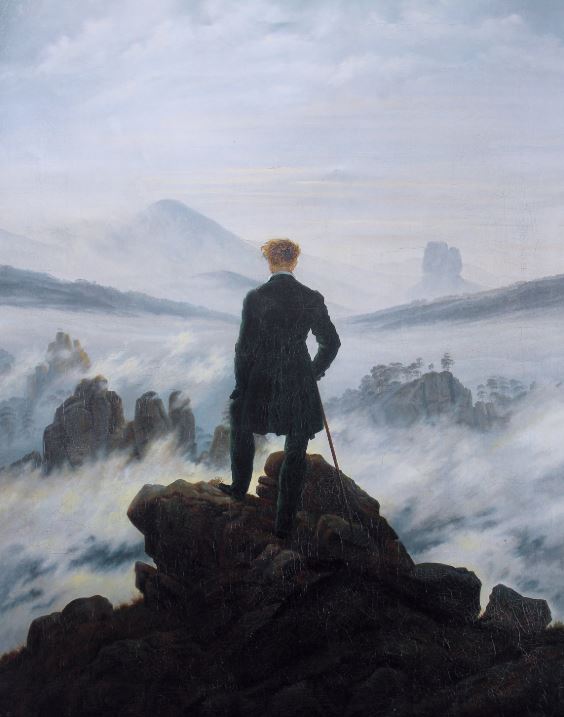

2. Emphasized emotions and individualism
Romanticism placed a strong emphasis on emotions as a driving force for creative expression.
Artists of this movement believed that emotions, including love, passion, fear, and awe, were not only valid but essential sources of inspiration. They aimed to capture and convey these intense feelings in their works.
Also Read: Romantic Period Timeline
For example, in paintings, artists often depicted dramatic scenes that evoked powerful emotions, such as the anguish of lost love or the awe of a breathtaking natural landscape.
3. Celebrated the beauty and power of nature
Nature was a central theme in Romantic art. Romantics were deeply influenced by the beauty and majesty of the natural world. They often depicted landscapes, forests, mountains, and seascapes to convey the sublime power and grandeur of nature.
These depictions aimed to evoke a sense of wonder and awe in the viewer. Romantic artists believed that a close connection to nature could inspire creativity and provide a spiritual connection to the universe.
4. Explored the concept of the sublime in nature
The concept of the sublime was a significant theme in Romantic art. Romantics believed that encounters with vast, powerful, and often awe-inspiring aspects of nature, such as storms, towering mountains, or tumultuous seas, could evoke a profound sense of the sublime.
These experiences stirred feelings of wonder, fear, and reverence, and artists sought to convey these emotions through their work.
Paintings and literature often depicted scenes where individuals confronted the sublime forces of nature, emphasizing the smallness of humanity in the face of such majesty.
5. Focused on the unique experiences of individuals
Romanticism celebrated the individual and their unique experiences, beliefs, and emotions. This emphasis on individualism was a reaction against the conformity and rationalism of the Enlightenment era.
Romantic artists often depicted heroic individuals who defied societal norms, often with tragic consequences. These characters were seen as symbols of individualism, freedom, and rebellion, embodying the idea that personal emotions and experiences held great value.
6. Contributed to the development of national identities
Romanticism played a significant role in shaping and promoting national identities in various European countries. Artists drew inspiration from their own national cultures, folklore, and history, leading to a resurgence of interest in national heritage.
This cultural revival helped foster a sense of belonging and unity among people within their respective nations. For example, the Romantic movement in Germany, known as German Romanticism, celebrated German culture, folklore, and history.
7. Showcased exotic and distant cultures
Romantic artists were often fascinated by the exotic and the unfamiliar. This fascination led to the portrayal of distant lands, foreign cultures, and non-European traditions in their works.
Paintings, literature, and music often featured scenes or characters from far-off places, contributing to a sense of adventure and curiosity. This exploration of exotic themes also reflected the era’s interest in exploration and the expanding global reach of European powers.

8. Inspired by medieval and Gothic styles
Romanticism witnessed a revival of interest in medieval and Gothic aesthetics. Artists drew inspiration from the architecture, art, and literature of these historical periods.
Gothic cathedrals, with their soaring spires and intricate details, served as symbols of the Romantic fascination with the mysterious and the sublime.
This revival in Gothic and medieval styles contributed to the creation of art that emulated the romanticized aspects of these historical eras.
9. Influenced by Romantic literature and poetry
Many Romantic artists were deeply influenced by the literary works of their contemporaries, particularly the poets of the Romantic movement.
Poets like William Wordsworth, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, Lord Byron, and John Keats explored themes of nature, emotions, and individualism in their poetry.
These literary works inspired painters and composers to create visual and musical expressions of the same themes. For example, Caspar David Friedrich’s paintings often evoke the same sense of wonder and awe found in Wordsworth’s poetry.
10. Featured heroic and often tragic figures
Romantic art often featured heroic figures who struggled against adversity, often with tragic outcomes. These figures, whether historical or fictional, were seen as embodiments of the Romantic ideals of individualism, passion, and rebellion.
For example, the painting “The Death of Sardanapalus” by Eugène Delacroix portrays the tragic and heroic death of an Assyrian king, highlighting the intense emotions and chaos of the scene.
11. Depicted rural landscapes as an escape from urbanization
As industrialization transformed cities and brought about social and environmental issues, Romantic artists often depicted rural landscapes as a retreat from the negative aspects of urban life.
These serene and idyllic landscapes represented an escape to a simpler, more harmonious existence in nature. Artists like John Constable in England and the Hudson River School painters in the United States celebrated the tranquility of the countryside.
12. Emphasized vibrant colors and imagination
Romantic painters placed a strong emphasis on color and the use of vivid, emotive palettes. They sought to convey the intensity of emotions through their choice of colors and brushwork.
Additionally, Romantics often relied on their imagination to create fantastical and dreamlike scenes that went beyond realistic representation. This emphasis on imagination allowed artists to explore inner emotions and fantasies.
13. Left a lasting impact on subsequent art movements
The influence of Romanticism can be seen in various art forms that followed, including Impressionism, Symbolism, and even aspects of modern art.
The focus on emotion, imagination, and individual expression continued to shape the way artists approached their work in the years that followed. Romanticism remains a pivotal movement in the history of art and culture, influencing subsequent generations of artists and thinkers.

