For many people the different types of art, art movements and art styles can be a little overwhelming and often the language used within the art world somewhat confusing……
Art movements are ways that art evolves over time. The four most popular art movements are surrealism, impressionism, realism and abstract expressionism.
There are many philosophies that are used when creating art that are often categorized into different movements. These philosophies can range from modernism, postmodernism, and post-structuralism to name a few.
Types of Art Movements
Abstract Expressionism

Abstract Expressionism is an art form that is not confined to realism. It is an attempt to paint what is felt rather than what one sees. The complete focus on the feeling of a painting and its brushstrokes can be seen in Abstract Expressionist paintings.
It is a style of painting that emerged in the 1940s, in New York City. The movement was led by artists such as Jackson Pollock, Willem de Kooning, and Mark Rothko.
Emerging at the time of World War II and thus many people think its purpose was to express raw emotion for those who were unable to express themselves because of what happened during this time period.
Abstract expressionists were deeply concerned with the expressive use of color and form, often such as with the use of all-over technique and was a radical departure from traditional Western painting.
Aestheticism Art

Aestheticism is an artistic and literary movement that originated in the second half of the 19th century in England and spread to the rest of Europe.
Aestheticism grew as a reaction to positivism, which asserted that art should represent factual reality. It was not only a rejection of existing trends in painting and literature but also a rebellion against industrialization, urbanization, and the loss of tradition.
The arts were seen as a way to stimulate moral and emotional states in life. Aestheticists met regularly for meetings with their own set of beliefs, called “the credo”. These meetings were called “aesthetic tea parties”.
The movement was, at its core, a reaction to the ugliness and lack of beauty that was prevalent in Victorian England.
Also Read: Famous Victorian Paintings
The Aestheticists felt that the world had lost its sense of beauty, which they attributed to Christianity’s emphasis on humility. They sought to return society back into harmony with nature by using art for pleasure.
Aestheticism died out in the 20th century but had a huge impact on modern art. It was one of the inspirations for Impressionist painting.
Art Noveau

Art Noveau is a French term that means “new art”. It was an artistic movement, characterized by the use of fluid, organic lines. Art Noveau artists sought to create works that were more naturalistic and sensual.
It was an international architectural and decorative style that developed in the late 19th century in France. The style is characterized by a return to elaborate, flowing, organic forms influenced by nature and medieval art, as well as an appreciation of the decorative arts.
The important concepts of Art Nouveau are unity in variety, asymmetry, free-flowing lines and curves, stylization of plant forms with animals acting as their natural counterpoints or refined representations. The movement spread across Europe and was popularized in America partly through the work of American artist Louis Comfort Tiffany.
The style started to decline at the beginning of World War I and quickly disappeared after the war because of its association with decadence and frivolity.
It is said to have been inspired by the Japonisme movement, which was popular in France after the Japanese victory against Russia.
It was one of the first art styles to be called “modern”. It was a break from traditional 19th century art due to its focus on decorative arts and natural forms instead of realism.
The style reached the peak of its popularity during the Belle Epoch of 1900s-1910s before being replaced by Art Deco.
Avant-garde

Avant-garde art is a term which was coined in 19th century France. It refers to the work of artists and art movements that are characterized by their radical departure from traditional forms of representation.
Many artists use avant-garde techniques to provide insight on society, even though they are not always understood or appreciated. A form of modern art which is often shocking or offensive to people using traditional standards.
Avant-garde art is often described as being experimental, and it has been described in various ways, including as an “artistic revolt against the principles of order and harmony”, as “an attack on conventional notions of beauty and the traditional functions of fine art,” and as an exploration of the “psychic process in self-expression.”
The movement was an antipode to what was considered mainstream.
Art Deco

The Art Deco movement was a style of design that was popular during the 1920s to the 1930s. The term ‘Art Deco’ is derived from the French, and it translates into English as ‘a style of art applied to decoration.’ This style emerged in France and then spread to Europe, North America, and Latin America.
The term itself was coined in 1939 by French art dealer Georges-Pierre Seurat to describe an exhibition of furniture designed in 1925 for the Paris Exhibition that year and has since been applied more generally to items such as jewelry, clothing, textiles, posters and buildings such as the Chrysler Building in New York City.
The architecture is characterized by its use of curves and geometric shapes. The ubiquity of Art Deco can be found in buildings, furniture, fashion, graphic design, sculpture- all aspects of life during this era.
This movement featured an emphasis on geometric shapes with a heavy Egyptian influence such as curved shapes with sharp edges. In addition to Egypt’s influence on this trend there was also a focus on using vibrant colors to express themselves through clothing or exterior motifs
Baroque
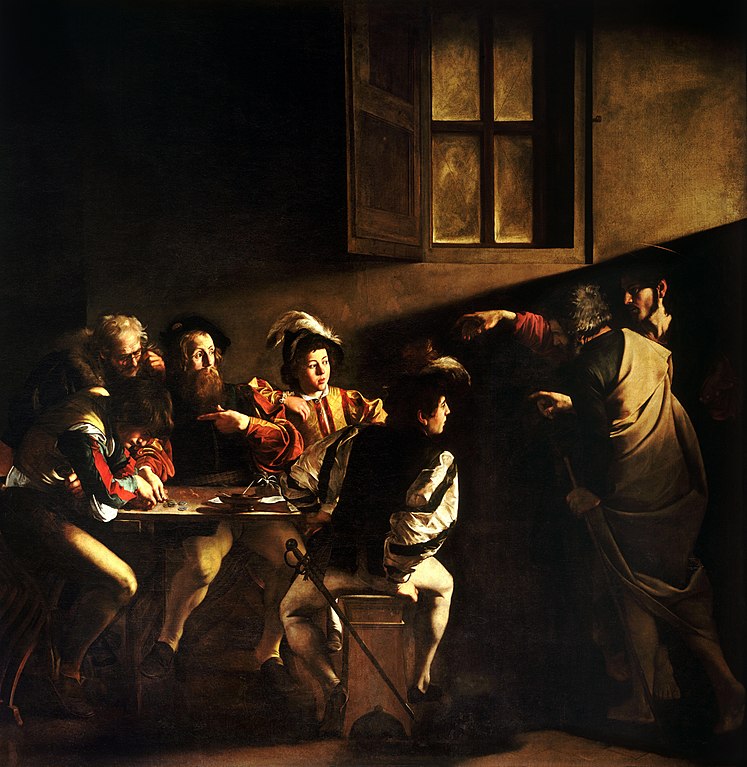

Baroque art is a term that describes an artistic period in Western Europe from about 1600 to 1750. The adjective baroque is derived from the Portuguese word barroco, meaning “misshapen pearl” with a possible connection to the French word barocque with similar meanings, and it is sometimes used pejoratively.
It is characterized by the use of dramatic and emotional subjects, the use of movement, and large scale.
Baroque originated in Rome around 1600 and spread quickly to Catholic countries. It ruled the arts until around 1760 when it gave way to Rococo and later Neoclassical styles. Baroque was applied to music, architecture, opera, painting, sculpture and other arts.
It emerged in Italy as a reaction to the Renaissance style which is often considered to be cold, emotionless, and too perfect. It was influenced by artists like Michelangelo and Caravaggio who emphasized the imperfections in human beings and their drawings of people.
Classicism
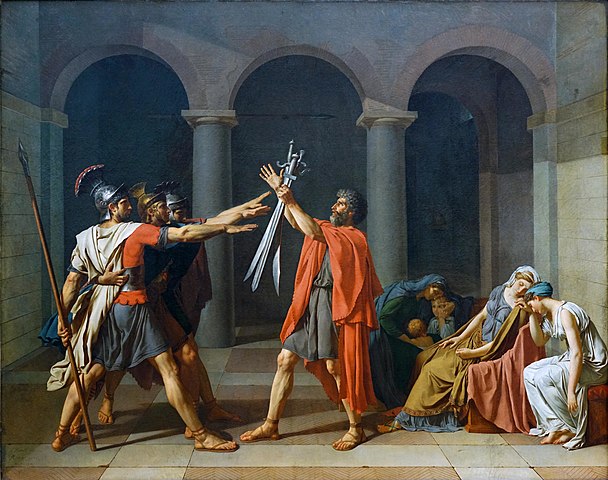

Classicism is an artistic style that was popular in Western Europe from 1750 to 1830.
This art style is a reaction against the dominant Baroque and Rococo styles of the time. It uses simple forms, clean lines, and often has a symmetry or order to it.
It was developed in Rome as a way to imitate the Classical Greek art.
Classicism can be described as the use of simple, clean lines and forms to create human-like figures and objects. The style was popularized by artists such as Jean-Baptiste Regnault, Robert Lefebvre, and Jacques Louis David.
Artists tried to emulate the artistic styles of classical antiquity, for example, ancient Greek and Roman sculpture. It was also a reaction against baroque style, which had been popular for over 100 years at that point.
An example of Classicism is The Death of Socrates by Jacques Louis David.
Collage

Collage art is the process of creating an artwork by taking different elements and arranging them into a cohesive whole. This typically entails cutting or tearing pieces of paper or other material and arranging them on a surface to create an image.
The word collage is French for ‘pasting’, therefore the artwork is created by pasting pieces together to form something new.
The idea behind collage art is to take various items and re-arrange them in an original way. In order for this to work, it needs to be executed in a creative manner that captures the attention of viewers.
Collage can be used to create a visual narrative or express an idea. A piece of art created through collage is called a collage. The word collage comes from the French word “coller” which means “to glue.”
Collages can be made with many types of materials, from pictures to buttons and hand-painted pieces of fabric.
A traditional way that artists create collages is to take two or more objects and put them on top of one another so that they overlap in order to form a new image.
Conceptual Art

Conceptual art is a type of art that communicates an idea or message, rather than represent physical objects.
The term “conceptual art” was coined by the artist and critic Lawrence Alloway in the mid-1960s, who used it to refer to the work of certain artists who were involved in the Fluxus group.
It has since used to describe any artwork, visual or otherwise, that intends to communicate an idea or message without being confined by a traditional medium or style.
Conceptual artists often use indirect means of expression, such as installations, photography, video, drawings and text-based work. Conceptual art shares with both abstract expressionism and minimalism the idea that all meaning comes from within the artwork’s physical materiality, not from some external source.
It consists of anything that focuses on conceptual rather than physical reality. Some examples of this are Marcel Duchamp’s Fountain, Yoko Ono’s Cut Piece or just a plain white canvas with a label that says ‘This work is called white canvas’.
In many ways it resembles the avant-garde tendencies in the late 19th century, and developed out of it to become more radical in terms of its approaches to meaning and aesthetic value. Conceptualism often takes the form of a critique aimed at traditional concepts like “art” and “truth”.
Constructivism

Constructivism art is a style of art that emerged from the Russian Constructivist movement. The artists who work in this style believe that the art is an abstract, objective truth and their goal is to show the world as it really is.
The concept of constructivism was first developed by an artist and designer known as Vladimir Tatlin during 1920s. He was influenced by the ideas of Russian futurist and constructivist poets. He wanted to create a new kind of art which would be dynamic, free from any type of restrictions, political or otherwise.
It was inspired by Vladimir Lenin’s idea that art should be used as a tool to spread communist ideology. Constructivists looked at the world with an analytical eye and rejected the objectivity of pure art.
They wanted their art to express what they believed life to be about – joy, happiness, urban life and so on. In doing so they tried to create new forms and techniques that would help them communicate their ideas more clearly in order to provoke thought among viewers.
Contemporary Art
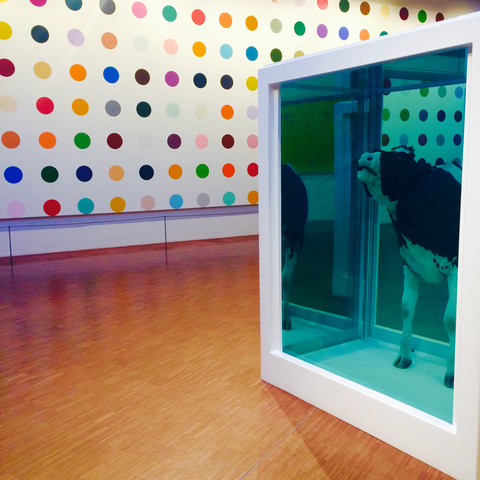

The term “contemporary art” is used in the art world to differentiate between modern and postmodern forms. The contemporary movement is characterized by abstraction, minimalism, conceptualism, and installation art.
Contemporary artists often use new technologies to produce their work of art. They are always exploring new possibilities for their art.
It has been evolving in the past few decades to become a form of artistic expression that is not constrained by any traditional ideas or norms.
Contemporary art is not defined by one specific style, but rather a movement that strives to be innovative and experimental. The best way to define contemporary art is to consider it as an entity of its own and not just the result of the past styles merged together.
Cubism
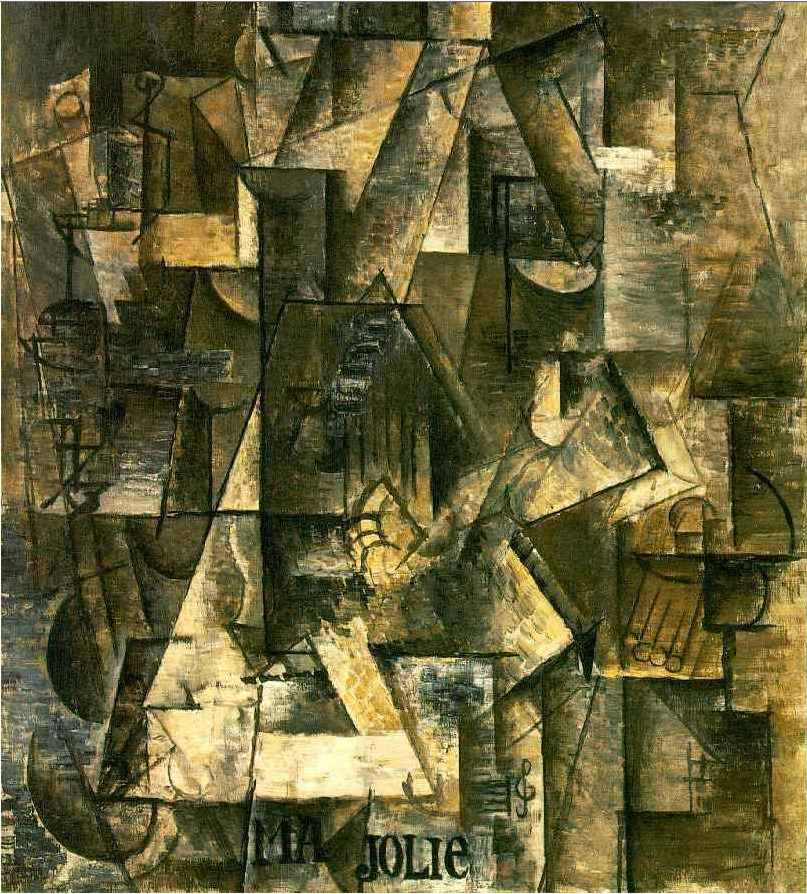

Cubism is an influential avant-garde art movement that started in France in the early 20th century. Cubists are focused on the idea that objects are seen from many different angles at the same time. They used art to represent what they saw as they looked at objects from different perspectives.
Also Read: Different Types of Cubism
Cubism artists believed that a painting or sculpture should be a collection of objects, not just one object seen from one view. They believed that we see objects every way, so why not show them all?
Some of the most famous Cubists were Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque who created paintings like ‘The Violin’.
They both started to experiment with depicting objects from a number of different points of view at the same time, with pictures that were created from paint on a two-dimensional surface.
Cubism was influenced by African tribal masks and Iberian sculpture as well as Cezanne’s analytical painting techniques which were used before Cubism became popular.
Dada / Dadaism

Dadaism is a cultural activity that was born in the aftermath of World War I. It emerged from the coffee houses in Zurich, Switzerland where artists would meet to discuss the war’s atrocities and their impact on society.
It was a movement that defied any traditional notions of order, logic, and sincerity in the arts.
Dada means “hobbyhorse” or “a child’s beggar’s staff with horse head.” Dada is an anti-art form that purposely uses irrationality and nihilism as its main devices to achieve their goal of rejecting what they saw as an overly bourgeois society.
Dada artists wanted to create work that would horrify beauty lovers and show them the absurdity of war. They have been described as having a “wicked sense of humor” which they use to critique society through poetry, sound poems, paintings, sculptures, collages etc.
Expressionism

Expressionism is a modernist art movement that originated in the early 20th century in the Netherlands and Germany. It is broadly a style of visual art, literature, theater, film and music which seeks to express emotion or ideas through extreme distortion of form or content.
In other words: it is an art movement that came into being as a reaction to Impressionism’s limitations in capturing emotional conditions.
An example of Expressionism can be seen in Vincent Van Gogh’s “The Starry night” painting which embodies the artist’s emotional state on the particular day he painted it.
Expressionist artists sought to express emotional experience rather than physical reality. They focused on the inner world of human beings rather than the outer world of objects.
The movement emerged as a response against nineteenth-century realism and naturalism, which focused on external visual reality. Expressionists experimented with new ways to show feelings and emotions, and sought to represent them visually.
Fauvism

Fauvism was an artistic movement between 1905 and 1914. It is characterized by the use of unnatural colors, such as yellow, pink and purple. A key feature in the paintings of Fauves is the use of pure colors in bright sunlight.
Fauvism is a style of painting that got its name from the French word “Fauve” meaning “wild beast.”
The movement began in France when Henri Matisse was inspired by a piece of African art that he saw at the home of his friend and artist André Derain.
Matisse became interested in this art form after viewing a similar piece at exhibitions sponsored by Paul Durand-Ruel since 1895. The paintings were characterized by their simplified shapes, broad strokes and high-keyed colors which contrasted greatly with Impressionist paintings which had somber subjects rendered in muted tones.
The Fauves were interested in color for its emotional and expressive qualities rather than for its symbolic or naturalistic associations. They abandoned all academic rules and devoted themselves to fresh, spontaneous expression in the moment. It is characterized by bright colors that create an emotional response in viewers.
Feminism Art
Feminism art is a form of art that aims to critique the social norms, stereotypes and expectations of women.
Feminism in art was initially a rather controversial topic but as more artists used this form of expression, it became more accepted. The Feminist movement has always been there and it is just now that we are starting to see a change.
While there are many definitions for feminism, all of them have something in common: the idea that women should have the same opportunities as men. This can mean different things depending on who is defining feminism.
Yet, it is not always easy to know what feminism art is. There is no specific definition of what feminism art should be and there are a lot of different perspectives about this subject. But one thing that most people agree on is that those who create feminist art should support the feminist ideals in some way.
Fluxus

Fluxus is an international group of artists, composers, designers and poets that was established in New York City in the early 1970s.
It was largely an American movement with strong links to the European avant-garde.
The term ‘fluxus’ was coined by George Maciunas, one of the key figures in the Fluxus art movement, to designate his group of artists and their work and its relations to other art movements such as minimalism, conceptual art, and visual poetry.
Fluxus artists rejected previous art conventions such as traditional materials, size or shape. They wanted to create a new form of art which is personal, visual and subjective.
The term fluxus has two meanings: it can refer either to the wider oeuvre of any fluxus artist or to one specific work by a particular artist.
Futurism

Futurism art is a form of art that started in Italy in 1909. The Futurists were a group of artists who wanted to break free from the artistic traditions, so they experimented with new techniques like Cubism and Expressionism.
It was mainly led by the poet and artist, Filippo Tommaso Marinetti.
The term futurism came from the French word “futur”, which means future. The Futurists wanted their art to show what life would be like in the future. They were especially interested in modern technology, so they had images and videos of trains, airplanes and automobiles.
Futuristic art is art that draws its inspiration from the future. These artists try to imagine what the world could look like in a few decades or even centuries.
Futuristic art is a subset of science fiction, but it’s also an aesthetic that can be used for other purposes than depicting imaginary worlds.
It often depicts what the artist believes to be possible with current technology, but it can also be based on ideas from imagination and research in fields such as technology, science and space exploration.
This genre of art has been seen in many films and books as well as actual paintings and sculptures around the world.
Geometric Art

The term “geometric” is used to describe this type of art because the shapes are often geometric and angles, circles, squares, or rectangles are often seen as well. Geometric art can come in all forms of media like sculpture or painting but most typically comes in the form of paintings or drawings on paper.
There are three types of geometric artworks: abstract geometric artworks, representational geometric artworks and graphic design
Abstract Geometric Art: the artist tries to express his own thoughts or feelings by creating form through the use of geometrical shapes in an abstract way.
Representational Geometric Art: the artist tries to represent objects or ideas that exist in reality by using geometrical shapes in a more realistic way.
Graffiti
Graffiti is a form of visual art that is done typically in public spaces. Graffiti artists use aerosol paint, markers, or other tools to create images and text on walls and in other public spaces.
Graffiti has existed for centuries and it is a very old art form from the beginning of civilization. The earliest form would have been with prehistoric cave paintings.
Modern graffiti was created to cover up advertisements in the 1960s. It can be used as a legal way to display one’s opinions about an organization or institution, such as through protest or commentary, and it can also be used as illegal vandalism.
Hyperrealism
Hyperrealism is a specific genre of painting and sculpture that is not abstract. The artist must be able to represent the subject realistically, but the goal of hyperrealism is to make the art so life-like it looks like a photograph.
The term was coined by Arthur Michaelovitch in 1968, who stated: “Hyperrealism is the deliberate use of techniques designed to make a painting look like a photograph”. Technical skill is required on behalf of the artist for this style, as it relies on close study and representation rather than abstraction or experimentation.
The paintings are so realistic that they seem real, or hyperrealistic. They make the viewer believe in the reality of what he or she sees, but in reality it is just an illusion created by paint on canvas or polystyrene on wood.
Impressionism

Impressionism is an art movement that aims to capture the subjective and universal impression that an observer has from a scene. The movement is characterized by the technique of using small, mobile brushstrokes, as opposed to the more common practice of applying paint in a uniform manner.
Some famous impressionist painters are Claude Monet, Edgar Degas, and Pierre-Auguste Renoir.
The term “impressionism” was first used by art critic and historian, Édouard Dujardin, in 1863. He used the term to describe Monet’s paintings made during the winter of 1860-61, which were characterized by unusual color and light effects.
Impressionism is characterized by visible brushstrokes, an artist’s use of color, and attention to detail. The impressionists try to show how light affects people and objects, how surfaces look under different lighting conditions such as dawn and dusk, or how shadows change with time.
Installation Art

Installation art is art that is created for a specific space and time.
Installation art can explore the concepts of life, death, and nature. It can be interactive, such as asking viewers to step on a plank of wood to create a sound when they walk across it.
The artist could also use installation art as a way to explore ideas in the world around them. It’s often participatory or interactive in nature.
Installation art started to become a trend in the late 1960s with artists exploring new ways of displaying their work. The goal of installation art is not to create an aesthetic display but instead to create an immersive experience.
They are interactive pieces that are designed to be experienced by the public rather than just seen in a gallery setting. Installation art often uses site-specific features such as architecture, sculpture, maps, and sound or light projections.
It is often constructed in non-traditional spaces such as museums, galleries, or private homes and can range from large-scale sculptures that take up an entire room to tiny hidden objects tucked away in obscure corners.
Landscape Art

Landscape art or landscape painting is the act of depicting a landscape, or making an accurate representation of an area of natural scenery, especially in watercolor.
It is the combination of two words “land” and “scape”. These two words are often used to define different things but in this context they are both referring to the same thing. Landscape art is a form of painting that depicts landscapes, usually in nature, and is done with watercolor paints. The word “land” means scenery and the word “scape” means paint.
This type of art originated from long ago when ancient people would use this as a way to keep their memories of home alive while they were away for long periods at a time.
Landscape Art is a painting, drawing, or print of landscape. It is a term that encompasses rural landscapes, urban landscapes and natural scenes.
One of the oldest paintings of Landscape Art is the Garden of Eden. It depicts the world as it was before humanity’s fall from grace.
Medieval
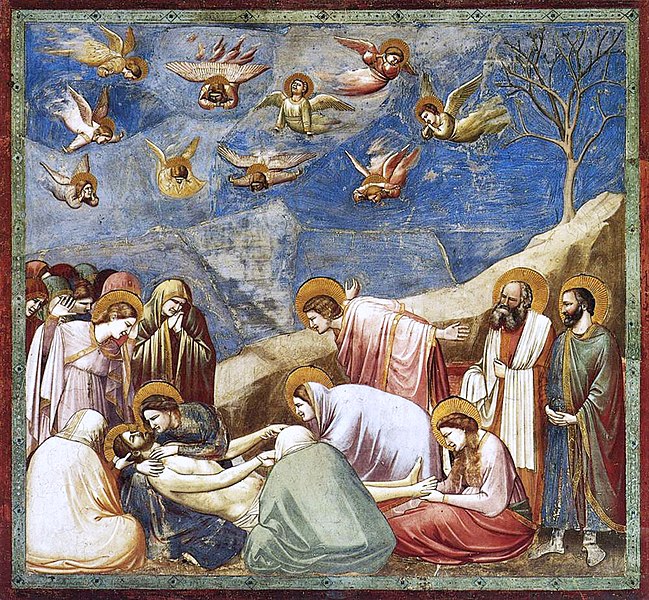

Medieval art is a broad term that refers to all the art produced in Europe during the Middle Ages. This was a period of time between about 500 and 1500.
Though there are many different types of Medieval Art, some of the most common are illuminated manuscripts, metalwork, sculpture, stained glass and frescoes.
The Medieval era was characterized by the revival of classical forms and the beginning of new social classes. This period is also known as the High Middle Ages and spanned from about 1000 to 1500 in Europe (Near East and North Africa).
In this time, artists were given more freedom to express themselves. This led to some of the most influential pieces of art during that time. The goal for these artists was to create a sense of spirituality in their work.
They wanted their work to be spiritually uplifting because they believed that through art, people could better understand Christianity and find salvation.
The idea for these pieces originated from religious paintings which were used during Medieval Masses called “The Masses”. These paintings were done on wood panels which would then be attached on church walls or alter
Minimalism

Minimalism is a style that became popular in the early twentieth century. The art form is based on a few simple geometric shapes, such as lines and rectangles. Minimalism uses these shapes to create beautiful artwork.
The term Minimalism was coined by American art critic and writer Donald Judd in 1968. Since then, the art movement has been adopted by many artists all over the world.
Minimalism is a form of art that strives to attain maximum results with minimum means. It is an artistic style that came about in the late 1950s and early 1960s, primarily in America and Western Europe.
This form of art is characterized by reductive geometric forms often set against a white or light-colored background. The artist’s goal in this style is to present a sense of order, clarity, balance, and restraint or calmness through reducing complexity or ornamentation to its simplest shape or form.
Mannerism

Mannerism is a style of painting and sculpture that emerged in Rome during the 1520s and spread to most of Europe.
It takes its name from the Italian word maniera, meaning “style” or “manner.”
The mannerist artists rejected the smoothness and clarity of earlier Renaissance art, as exemplified by Leonardo da Vinci. They also sought to give their works an emotional intensity that made them greater than reality.
Mannerism can be seen as a form of extravagance on Renaissance culture, with its fine arts becoming more complex and intellectualized than they had been since antiquity.
The style is characterized by elongated and highly stylized figures, often with an unnatural degree of emotion or sexuality; dramatic gestures and poses; contrasting coloration; and a “restrained intellectual quality”.
Naivism
Naivism is a global artistic movement that began in the 1970s. It is characterized by its use of bright, cheerful colors and childlike imagery with happy subjects (for instance, flowers and trees).
The Naive artists paint scenes from their daily lives: family gatherings, animals, still life compositions.
The word Naïve is derived from the French word “Naïf,” which means “simple.” And this refers to the more simplistic qualities in their paintings.
Naïve artists try to depict their subjects with the most basic geometric shapes, without shading or detail.
Naturalism
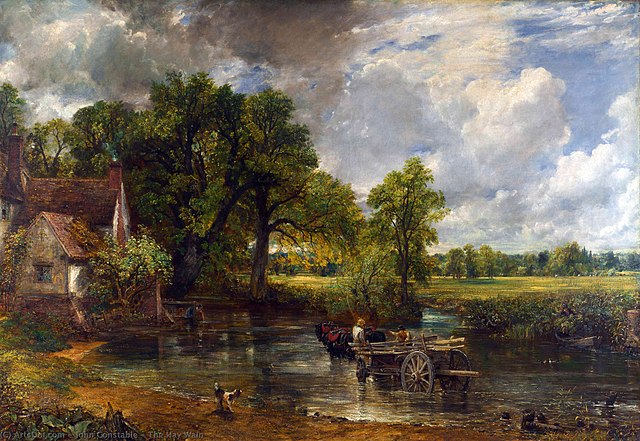
Naturalism Art is an international movement of realism in art, with the intention of showing objects and scenes as they are naturally. It was a reaction to Romanticism, which tended to exaggerate colors and details.
The term “Naturalism” can be applied to all forms of art that show objects and scenes as they are naturally. However, it is mainly used to describe painting from the mid-19th century through the late 1940s.
Naturalism artworks typically focus on the everyday lives and settings, often depicting rural scenes with country houses, farms, and crops. It avoids idealization and romanticism.
Neo-Classicism
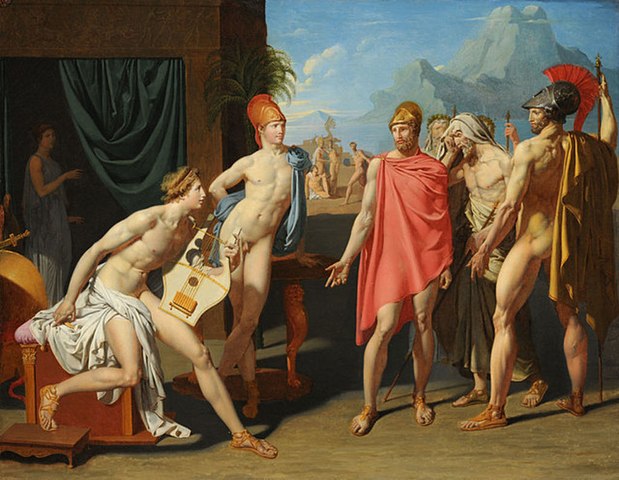

Neo-Classicism is a revival of the principles of ancient Greek and Roman sculpture and architecture. The term “neoclassical” comes from the 18th century and was originally a pejorative term.
The style can be seen in both paintings and sculptures, but it is mainly focused on painting as it requires more skill than in sculpting.
Neo-Classicism emerged in Rome, Italy during the 18th century, about two hundred years after neoclassical artists were first starting to make changes to their work. The style was popularized by the French Academy in 1750 as a reaction against rococo art which had been popular since the 1740s.
Neo-Classicists wanted to move away from Romanticism and return to the Classical era of art.
The most famous Neo-classicist artists are Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres and Eugene Delacroix.
Neo-Impressionism
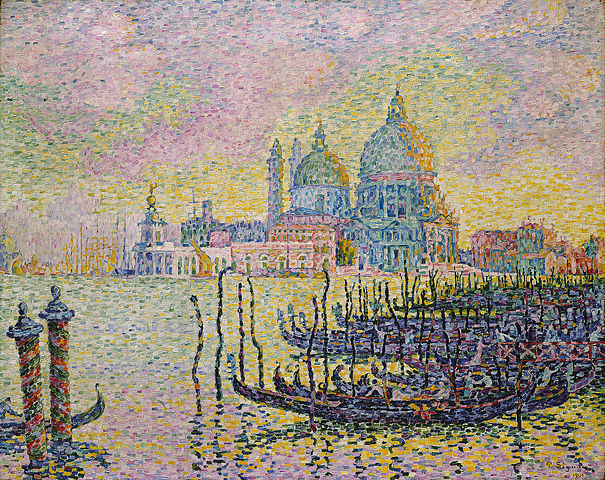

Neo-Impressionism art is a form of painting that was developed in the late 19th century. It is a style of painting that looks like impressionists, but with more defined brush strokes and brighter colors. It was created after the Impressionist movement, which started in 1874 and lasted until around 1886.
Neo-Impressionists wanted to reproduce an image in a moment of time and capture it on canvas just as it is seen by the eye.
In contrast to traditional painting techniques, they applied colors directly on top of one another without blending them first, which creates an intense color palette and more definite outlines than those found in Impressionist paintings.
Neo-plasticism
Neo-plasticism is a form of abstract painting that was pioneered by Romanian artist, Constantin Brancusi. He introduced the style in 1909 with his work “Bird in Space.”
It is a style that is characterized by flat planes, free composition, and strong colors. The name neo-plasticism was coined by the Romanian modern art critic and poet, T. P. Toma in 1929.
The movement was a reaction to the Impressionist and Cubist paintings of the era.
The new movement sought to eliminate all traces of recognizable or realistic objects from their paintings. They wanted the viewer to focus on color, shape, and composition alone.
Performance Art
Performance art is a type of art that challenges the traditional modes of communication by creating actions that are performed in front of an audience.
It’s been around for a long time and is not only popular in theater, but also in other art forms. Performance artists use their bodies, actions, or words to create their performances.
Performance Art is a type of visual art which has been around since the 1960s. It usually takes place in front of an audience and can involve any number of tools. It can be difficult to define what Performance Art actually is because it’s so diverse and there are many different types.
Pointillism
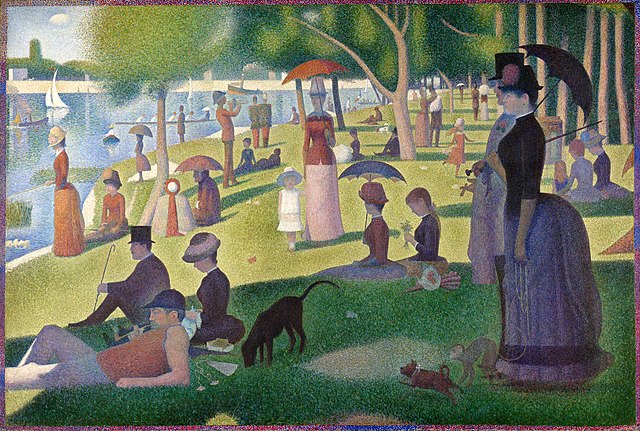
Pointillism is an art technique that involves the use of small dots of pure color to create the impression of a greater richness than is actually present.
It was born as an offshoot of Impressionism, a painting movement in France in the 1860s. The Impressionists wanted to communicate fleeting impressions, or moments, as they seemed to the artist.
They used short brush strokes and splashes of colors on canvas, but these were blended into a more unified whole by the viewer’s eye.
The Pointillist painters tried for a similar effect with small dots of paint instead of brush strokes and their work can be seen as an extension or refinement of Impressionism.
Pop Art
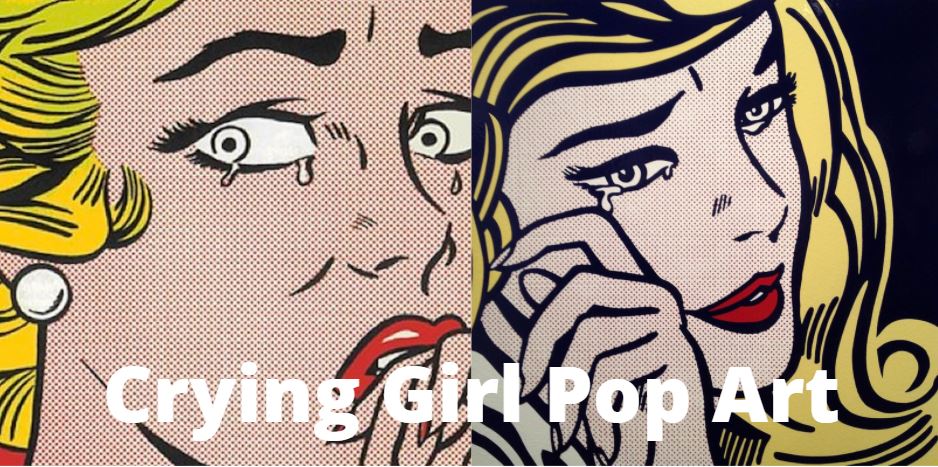
Pop Art is a term that was first coined in America to refer to a form of art that makes use of images from popular culture.
The Pop Art movement emerged in the 1950s and 1960s and was characterized by artists using bright, flat colors from commercial sources. Its origins can be found in the work of Jasper Johns, who produced works based on familiar symbols like flags, targets, numbers and letters.
Pop art is usually a mix of images and words that are taken from popular culture, such as movie stills or comic strips. These illustrations are then combined with other forms of popular culture such as advertisements, comic books and cartoons.
Portraiture

Portraiture is the most common form of painting in Western societies. A portrait artist is usually someone who specializes in creating portraits.
Portraits can be realistic or impressionist, and they can use any medium, but oil paintings are most often used because of their rich colors and textures.
Portraiture has its roots in the European tradition of painted allegorical and mythological subjects from Classical Antiquity, such as Plato’s Socrates or Aristotle’s David.
The tradition developed during the Renaissance, when artists would paint ennobled portraits of their patrons.
Post-Impressionism

Post-Impressionist painters used vivid colors, alternative brushstrokes, and new ways of representing solid objects to create a more expressive appearance than what was seen in Impressionist paintings.
The artists created their work by building on the advances made by Monet, Renoir, and Pissarro. They also took what they had learned from Symbolism and the Decorative Arts movement of the late 19th century.
Post-Impressionism is an art movement that emerged in the 1880s. It developed as an extension of Impressionism and is seen as a response to the naturalistic depiction of objects in Impressionist paintings. Common features of Post-Impressionist painting include a lack of distinct outlines and bold, broad brushstrokes.
Artists who followed this movement include Vincent van Gogh, Édouard Manet, Paul Gauguin, André Derain, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Maurice de Vlaminck and Georges Seurat.
Primitivism
Primitivism is an artistic movement that was born in late 19th century. It was a response to the cultural and political developments of the time, mainly the Industrial Revolution and European Modernism.
It can be seen as a reaction to industrialization, consumerism, and materialism.
Primitivists often use symbols from tribal cultures or other traditional art forms to critique modern life.
It refers to the tendency to emphasize, exaggerate, or even adopt a wilderness quality and style. Primitivist artists reject traditional standards of civilization and instead try to depict their idea of human nature in its purest form, often through drawing inspiration from pre-industrial folk art and childlike scribbles.
Rayonism
Rayonism is a style of painting that was developed in the late 19th century, and one of the major styles in Russian art. It has been considered to be a bridge between Impressionism and Cubism, but it occupies an independent position …
Rayonism is a term coined by art critic and journalist Vladimir Stasov in 1891 to describe paintings by such artists as Konstantin Korovin, Arkhip Kuindzhi, Mikhail Larionov, Vasily Polenov and others. They painted what they saw – their sensations – on the canvas.
Realism
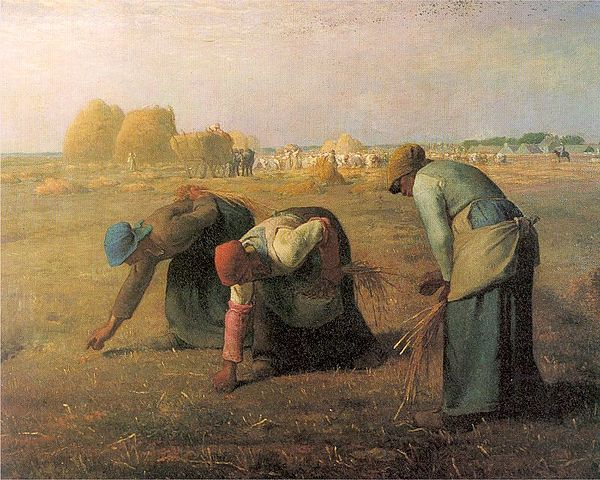

Realism art is a genre of art that strives to show things as they really are. It captures the everyday life and pays attention to detail.
The realism art movement started in the 19th century, when artists like Gustave Courbet and Édouard Manet were pushing against the bounds of traditional academic painting. They wanted to depict people in their lives and surroundings without idealizing them.
It often focused on the the lower classes in particular those that were engaged in heavy manual labor.
Renaissance

The word Renaissance means “rebirth” in Italian.
The Renaissance art movement was created during the European cultural revival period which started in the 1300s and lasted until the 1600s.
Renaissance art is a cultural movement that started in Florence, Italy.
The Renaissance artistic movement emerged from the medieval period. It was characterized by a return to classical styles of art and architecture, the study of natural sciences, and expression of thoughts through humanist philosophy.
Artists during the renaissance era were some of the first ones to use realistic representations in paintings. They started using perspective which led to more three-dimensional representations of objects on canvas.
The period was so named by art historians because it followed the medieval period and because it marked a “rebirth” of classical forms and ideas.
Renaissance paintings did not often portray biblical stories, but used allegorical symbols to convey messages about life. Subjects included scenes from Greek mythology as well as Christian themes such as the sacrifice of Isaac (see Poussin’s “The Death of Abraham”) or Jesus’ miracles. Artists in Renaissance paintings were also skilled at painting realistic textures, such as fabrics and fruits.
The Renaissance in Europe was characterized by a renewed interest in classical literature, an increased awareness of humanistic philosophy and science, and a rediscovery of ancient Greek and Roman knowledge. Artists during this time period were influenced by these new ideas and used them to create new forms of painting such as perspective or three-dimensional space.
More than any other era, the Renaissance was a time of intellectual and artistic ferment. Breaking free of the constraints and conventions of the medieval era, artists experimented with new techniques and ideas, giving rise to a magnificent outpouring of artistic achievement.
The Renaissance was a time when intellectual inquiry was at its peak. New ideas in science and philosophy were discussed as well as new innovations in art, architecture and literature. All these innovations led to an outpouring of magnificent artistic achievement.
Rococo

Rococo art is a European art movement which is characterized by lightness, elegant curves, ornamentation and asymmetry.
The term Rococo comes from the French word rocaille, which means ‘rock crystal’. Rococo art has a distinctive style and was popular in Europe during the 18th century. The style was inspired by lighter pieces of Baroque art and architecture, which were influenced by ancient Roman architecture as well as Renaissance artists like Raphael.
The paintings often depicted scenes that were full of movement with people dressed in elaborate clothing or dramatic scenes with intense emotions. The paintings also featured asymmetrical compositions with objects that appeared to be out of place or in some kind of tension with each other.
The Rococo movement was highly influenced by the Baroque and the Renaissance. Artists incorporated these influences in their paintings and sculptures.
Rococo art is born as a reaction to the Baroque period. Rococo artists put more emphasis on elegance and grace, while neglecting the seriousness of the subjects.
The Baroque art movement was based on an ornate and exaggerated style that was popular during the 17th century. The Rococo art movement is based on an intricate, decorative style that was popular during the 18th century.
The Rococo style was developed in France by artists Jean-Antoine Watteau, François Boucher and others.
Romanticism
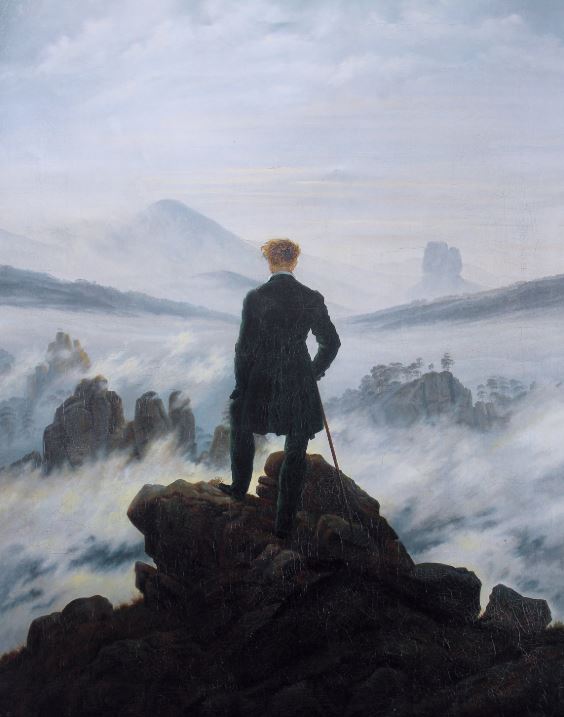

Romanticism was a literary and artistic movement that began in the late 18th century. It is characterized by a rejection of rationalism and an exaltation of emotion, imagination, freedom, and organic form.
Romanticism came about as a response to the Enlightenment belief that reason was more important than emotion to human life. The Romantics found emotion to be the reasoning factor in life and stressed personal liberty rather than social conformity.
The Romantic movement had different phases including early Romanticism (the period from 1800-1830) where works were primarily based on imagination; late Romanticism (the period from 1830-1900) where social reform became more prevalent; and post-Romanticism (1900-1910) when the movement largely died away with the rise of Modern art movements.
The movement developed in Europe as a reaction to Enlightenment ideas of reason, nature, and progress which it viewed as artificial constraints imposed by society on human creativity. It was embodied most strongly in art through paintings such as Caspar David Friedrich’s Wanderer Above the Sea of Fog (1818) or Victor Hugo’s Les Misérables (1862).
Still Life

Still Life art is a type of painting that captures the beauty of inanimate objects, like fruit, flowers, or household items.
The Still Life art has its roots in medieval Europe when artists would paint their own versions of nature. In the 16th century the still life genre was popular and painters began to paint more detail-oriented pieces that showed different perspectives and depths.
For example, Caravaggio’s “Basket with Fruit” is a composition of an arrangement of fruit in green baskets against a dark background that contributes to the mood and beauty of this piece.
Artists would often use food as their subjects because they were more abundant than other goods at the time. They also allowed for better lighting so artists could show color contrasts and details like textures.
“Still life” is the name for a painting that does not have any living things in it. It is usually just objects, flowers, food or dead animals.
The term “still life” comes from the French word “étude sur la nature morte.” This means that the paintings are studies of what happens when nature dies.
The goal of this type of painting is to create an impression with its objects (food, flowers, wine, and other goods) while depicting them as they exist in reality.
Street Art
Street Art is a form of art that is created in public spaces, usually outside and unsanctioned.
The street artist brings back the human element to the public space. They are not just some random person who has put up some graffiti on a wall; they are the voice and opinion of an individual who wants to make their voice heard. Street art is about having a message that can be conveyed to the world without any form of censorship.
Street art can take many forms and has grown to encompass more than just painting, as there are artists who have used a wide variety of media such as stickers, stencils, pastels, and wheat paste.
Surrealism
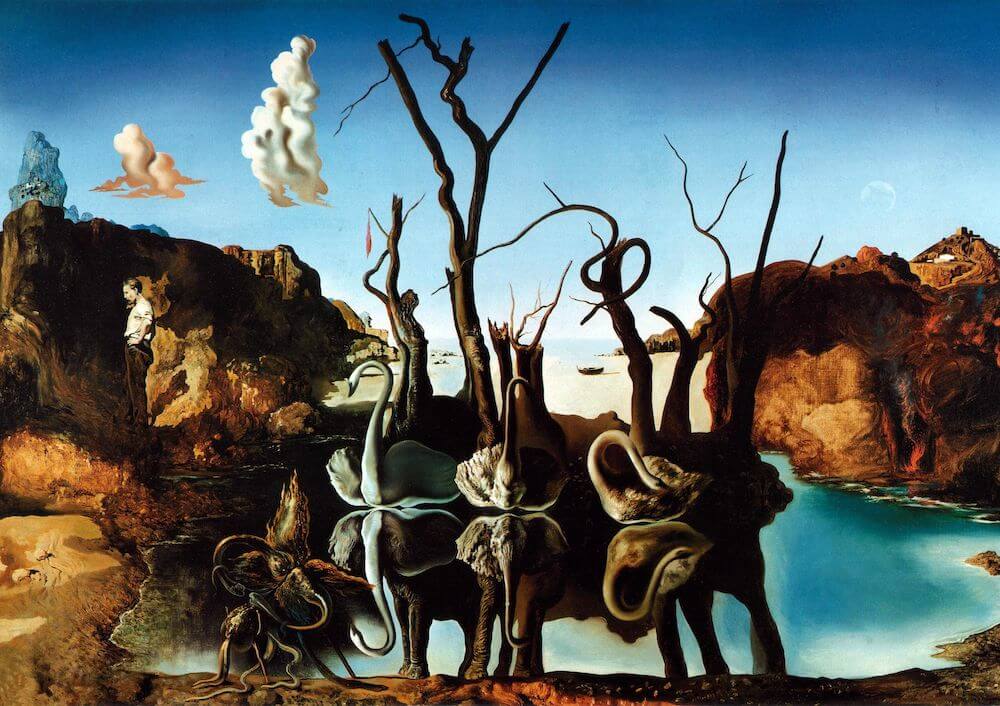

Surrealism is an art movement that emerged in the 20th century. It is a style of painting where the artist tries to represent the world by creating images that are impossible in reality.
The movement was started by Marcel Duchamp who wanted to mix something familiar with something unfamiliar and give it a new meaning.
Surrealism artists were influenced by Freudian psychology, which deals with the subconscious mind.
Some famous surrealist painters are Salvador Dali, René Magritte and Max Ernst among others.
There are many different types of art that fall under the umbrella of surrealism. This type of art is usually characterized by its dream-like qualities, and it often shows things in a distorted manner. Some common examples of surrealistic artwork include paintings, drawings, and sculptures.
One thing that people might not know about surrealism is that it also has ties to literature as well. One writer who was popular in the movement was Andre Breton, who wrote a pamphlet called Surrealist Manifesto back in 1924.
Suprematism
The term Suprematism refers to an abstract style of painting that originated in Russia in the early 20th century.
Suprematism is a trend in art, which evolved from Russian Futurism and Cubo-Futurism. It is based on geometric forms and colors, mainly black and white or red.
In its pure form, it produces a picture or design without any realism (representational art). Instead, Suprematism only uses shapes and colors to express an idea or concept.
It is based on the idea that the most basic shapes are enough to create a work of art, and that pure color and simple geometric shapes are more important than detailed lines or background colors.
The Suprematist movement was started by Kazimir Malevich in 1913 with his first Suprematist work called Black Square. Malevich’s idea was that a white square on a black background represented just about everything in life; time, space, being, or nothing.
Symbolism
Symbolism is an artistic movement in Western painting and poetry that was most active between 1880 and 1910. Symbolists were a reaction against naturalism and impressionism
Symbolism is a genre of art which seeks to express subjective meaning in an objective form. Artists typically represent objects such as the human body in symbolic ways, often using very stylized or exaggerated forms, colors, or proportions.
Symbolist works are often characterized by the use of symbols with complex associations to other ideas or images as their subject matter.
Symbolism Art can be found in various mediums including paintings, drawings, sculpture, photography and poetry.
A Symbolist usually conveys an idea by presenting it as a symbol which stands for another idea or some kind of abstraction. This is a kind of art that does not represent reality but instead expresses the inner feelings or moods from the mind of the artist.
Vorticism
Vorticism was a modernist movement in art that flourished from 1914 to 1918. The Vorticists wanted to create a new unity of the arts. They wanted to go beyond the conventional distinctions of the past and present.
Vorticism is a British art movement with a short life span, emerging just before World War I and lasting until about 1918. It is characterized by an abstract composition style that includes angular, linear designs with dynamic asymmetrical compositions, often reflecting an energetic or violent intensity.
Vorticism focuses on dynamism of form (rather than color) to portray sensation and ideas, which is what distinguishes it from futurism.
Vorticists believed that painting needs to be clear and simple because it represents objects; they believe that painting has its value only if it captures the instant.

